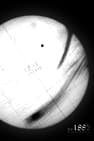
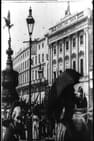Photo sequence of the rare transit of Venus over the face of the Sun, one of the first chronophotographic sequences. In 1873, P.J.C. Janssen, or Pierre Jules César Janssen, invented the Photographic Revolver, which captured a series of images in a row. The device, automatic, produced images in a row without human intervention, being used to serve as photographic evidence of the passage of Venus before the Sun, in 1874.
Telescopic chronophotography of the 1882 transit of Venus as observed from Lick Observatory.
The last remaining production of Le Prince's LPCC Type-16 (16-lens camera) is part of a gelatine film shot in 32 images/second, and pictures a man walking around a corner. Le Prince, who was in Leeds (UK) at that time, sent these images to his wife in New York City in a letter dated 18 August 1887.
Lost film from 1888, directed by William Friese-Greene.
The last remaining film of Le Prince's LPCCP Type-1 MkII single-lens camera is a sequence of frames of his son, Adolphe Le Prince, playing a diatonic button accordion. It was recorded on the steps of the house of Joseph Whitley, Adolphe's grandfather.
A horse with rider jumping over an obstacle. A scientific film made for the Prussian army to help their soldiers improve their horseback riding technique.
The earliest surviving celluloid film, and believed to be the second moving picture ever created, was shot by Louis Aimé Augustin Le Prince using the LPCCP Type-1 MkII single-lens camera. It was taken in the garden of Oakwood Grange, the Whitley family house in Roundhay, Leeds, West Riding of Yorkshire (UK), possibly on 14 October 1888. The film shows Adolphe Le Prince (Le Prince's son), Mrs. Sarah Whitley (Le Prince's mother-in-law), Joseph Whitley, and Miss Harriet Hartley walking around in circles, laughing to themselves, and staying within the area framed by the camera. The Roundhay Garden Scene was recorded at 12 frames per second and runs for 2.11 seconds.
A film by Louis Aimé Augustin Le Prince, shot in late October 1888, showing pedestrians and carriages crossing Leeds Bridge.
Alleged silent black-and-white short film shot at Apsley Gate, Hyde Park, London. It was claimed to be the first motion picture until pre-dating footage shot by Louis Le Prince was discovered. It was never publicly shown and is now considered a lost film with no known surviving prints or stills.
Hyde Park Corner (also known as Leisurely Pedestrians, Open Topped Buses and Hansom Cabs with Trotting Horses) depicts life at Hyde Park Corner in London. It is claimed to be the first film set in London, as well as the first to be filmed on celluloid. It is currently considered a partially lost film, with only 6 possible film frames preserved as part of the Jonathan Silent Film Collection.
One of the first movies ever made.
An early short film recording fencers.
Formerly lost film rediscovered in 1996, directed by William Friese-Greene.
Moving picture of London's Trafalgar Square traffic, filmed with a kinesigraph.
Shot of the flight of a fly.
Experimental film that follows up on the results of "Monkeyshines, No. 1". Once again, an Edison company worker moves around in front of the motion picture camera.
Experimental film made to test the original cylinder format of the Kinetoscope and believed to be the first film shot in the United States. It shows a blurry figure in white standing in one place making large gestures and is only a few seconds long.
Early film of men rowing on two boats.
This early cinematic instance of a close-up—or, more accurately, a medium close-up shot of the chest and face of the maker of this film and others like it, Georges Demenÿ saying “Je vous aime”—was made at the request of Hector Marichelle, professor and director of the National Deaf-Mute Institute in France, who planned to use filmed speech to teach deaf students to speak and lip read. This required close views of the performer's lip movements. The project was given to Demenÿ by Étienne-Jules Marey, who headed the Station Physiologique in Paris and whose chronophotographic scientific research of motion is among the most important contributions to the invention of movies. Despite these educational and scientific beginnings, however, this project led Demenÿ to pursue and influence the commercialism of cinema.
Short film of two men fencers